How to Calculate and Use the Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio Bench Accounting
But sometimes it could mean that the creditors of the company are excessive (bringing down the working capital) and this could be a problem in the future. Conversely, a low ratio could mean that there are too many debtors or a very big inventory which is not an efficient use of resources. Both of these ratios are significant in managing the debtors and bills receivables of a company. Not only do they calculate the velocity with which debtors pay up, they help shape the credit policy of the firm as well.
- Once you know how old your outstanding invoices are, you can work on it accordingly to increase revenue from them or also make a note of those who haven’t paid yet for further follow-ups.
- The higher the number of days it takes for customers to pay their bills results in a lower receivable turnover ratio.
- On the other hand, it could also be that your collection staff members are not receiving the training they need or are not assertive enough when following up on unpaid invoices.
- Once you have fixed the credit period for your clients make sure to follow up on them regularly until they pay their dues.
- Not only do they calculate the velocity with which debtors pay up, they help shape the credit policy of the firm as well.
How to Buy an Annuity: A Comprehensive Guide for Your Retirement Planning
We start by replacing the company’s “first period” of receivables with the January 1 data and “last period” with the information for December 31. Then we add them together and divide by two, giving us $35,000 as the average accounts receivable. As a rule of thumb, sticking with more conservative policies will typically shorten the time you have to wait for invoiced payments and save you from loads of cash flow and investor problems later on.
What Is Asset Turnover Ratio and How Is It Calculated?
It provides insights into how effectively a company manages its receivables and ultimately generates cash from sales. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll take you through the steps on how to calculate AR turnover, its importance, and how to improve it for better cash flow. The accounts receivable turnover ratio is a metric that assesses how quickly a business collects its payments from debtors during a specific time period, such as a month or a quarter. In essence, it compares your sales for a particular period with the amount owed to you during that time. Let’s say your company had $100,000 in net credit sales for the year, with average accounts receivable of $25,000.
How to Improve AR Turnover
This legal claim that the customers will pay for the product, is called accounts receivables, and related factor describing its efficiency is called the receivables turnover ratio. The accounts receivable turnover ratio, also known as receivables turnover, is a simple formula that calculates how quickly your customers or clients pay you the money they owe. It also serves as an indication of how effective your credit policies and collection processes are. The accounts receivable turnover ratio measures the number of times a company’s accounts receivable balance is collected in a given period.
A low ratio may also indicate that your business has subpar collection processes. On the other hand, it could also be that your collection staff members are not receiving the training they need or are not assertive enough when following up on unpaid invoices. Credit policies that are too liberal frequently bring in too many businesses that are unstable and lack creditworthiness. If you never know if or when you’re going to get paid for your work, it can create serious cash flow problems.
What does a low average accounts receivable turnover ratio mean?
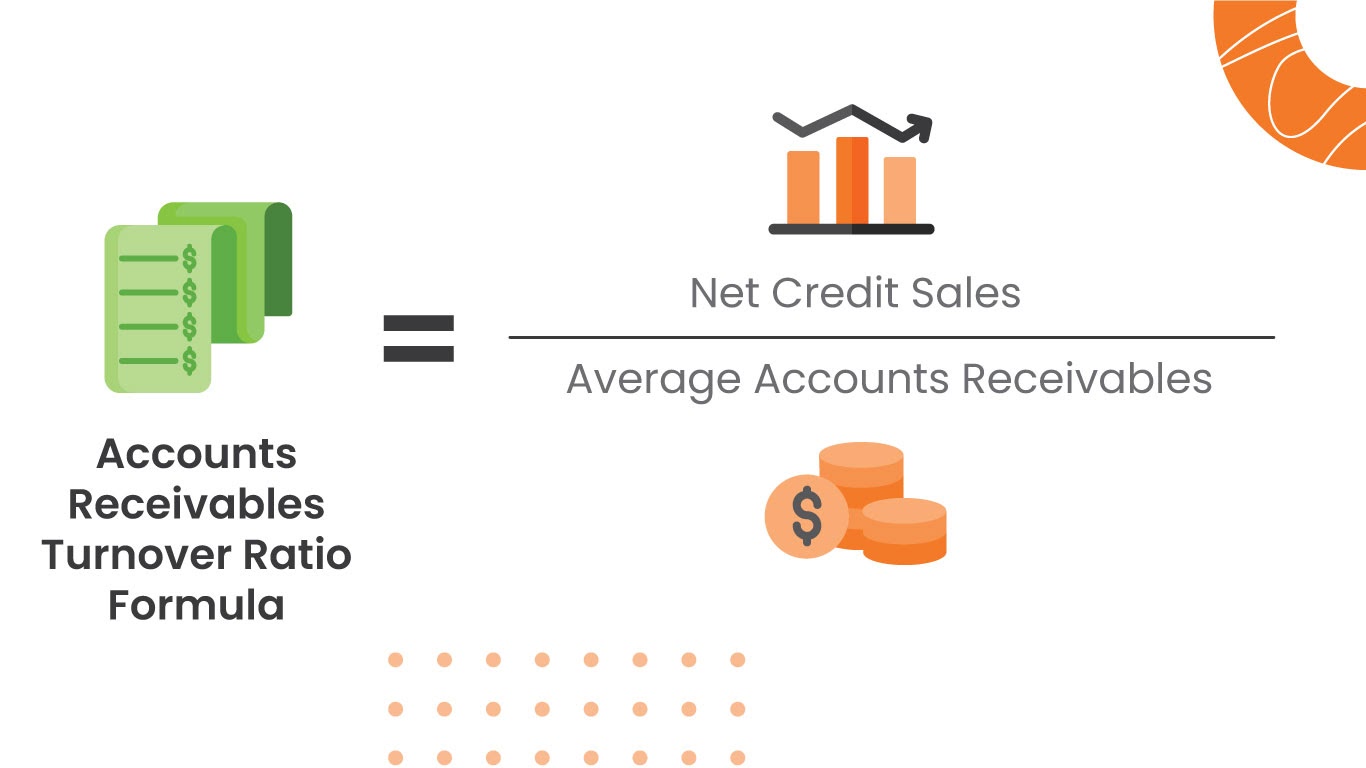
The accounts receivables turnover ratio measures the number of times a company collects its average accounts receivable balance. It is a quantification of a company’s effectiveness in collecting outstanding balances from clients and managing its line of credit process. Net credit sales is the revenue generated when a firm sells its goods or services on credit on a given day – the product is sold, but the money will be paid later. To keep track of the cash flow (movement of money), this has to be recorded in the accounting books (bookkeeping is an integral part of healthy business activity).
As can be seen from the receivable turnover ratio formula, this financial metric has quite a simple equation. The higher the number of days it takes for customers to pay their bills results in a lower receivable turnover ratio. This being said, in order to best monitor your business finances, accounting, and bookkeeping, we’d recommend investing in robust accounting software, like QuickBooks, for example. Lastly, when it comes to comparing different companies’ accounts receivables turnover rates, only those companies who are in the same industry and have similar business models should be compared. Comparing the accounts receivables turnover ratio of companies of varying sizes or capital structures is not particularly useful and you should use caution in doing so.
This figure does not include cash sales as cash sales do not incur accounts receivable activity. Net credit sales also incorporates sales discounts or returns from income tax return 2020 customers and is calculated as gross credit sales less these residual reductions. It indicates the speed with which the payments are made to the trade creditors.
Doing so allows you to determine whether the current turnover ratio represents progress or is a red flag signaling the need for change. When your customers don’t pay on time, it can lead to late payments on your own bills. Unpaid invoices can negatively affect the end-of-year revenue statements and scare away potential lenders and investors. Most businesses operate on credit, which means they deliver the goods or services upfront, invoice the customer, and give them a set amount of time to pay.
When you have specific restrictions for those you offer credit to, it helps you avoid customers who aren’t credit-worthy and are more likely to put off paying their debts. You can use this average collection period information to compare your company’s receivables turnover time with that of other companies in your industry. Use this formula to calculate the receivables turnover ratio for your business at least once every quarter. Track and compare these results to identify any trends or patterns that may develop. We calculate the average accounts receivable by dividing the sum of a specific timeframe’s beginning and ending receivables (most frequently months or quarters) and dividing by two. It represents the number of times AR is turned into cash within a specific period, typically a year.

